Leveraging AI for Safer Roads
Pothole Map Overlay
Pothole Reporting Feature
TIMELINE
November 2022
MY ROLL
Solo Project
SOFTWARE USED
Loom
PowerPoint
SUMMARY
Google Maps is an online mapping platform offered by Google. Google Maps offers a number of features for users and businesses to use. Within the application, users can view satellite imagery and street views of places all around the world. Google Maps is highly interactive and offers real-time information about traffic and road closures. Routing options are also included to customize directions to your mode of transportation (car, bike, foot, etc) and road conditions (traffic, stop-lights, tolls, etc).
This project uses AI and machine learning to automatically detect potholes in real-time as drivers navigate the roads by harnessing data from Google Maps users. The system alerts drivers to potential hazards and automatically generates reports for local authorities to prioritize repairs.
HUMAN-COMPUTER COOPERATION ANALYSIS
Human Actions and Skills Required to Complete the Task
There are a number of tasks users can complete while interacting with Google Maps like planning routes, using directions, viewing locations, searching locations, looking at business information, and more. One common task a user may find themselves trying to complete is to get directions to a certain location. For example, a user may try to get directions from their house to the nearest target store. This task involves cooperation between the user and the computer. To begin, the user must find the destination they want directions to, in this case, it is the nearest target. The user has a few methods they can use to find the desired destination. For example, they may type in the address or find the store by typing in “Target” and selecting the desired location or using the map to look around and find what location they are trying to get to.
Next, the Google Maps software can take their current location as their starting point or the user can input a different starting location. Google Maps software can then use detailed information about traffic, road work, and more to create optimal routes to the selected Target store. The user is then able to select the route they want and can start the directions to their destination.
Computer Actions and Capabilities Required
Google Maps has access to a wide range of information that users do not always have. It has access to information like traffic, wrecks, road closures, tolls, stoplights, stop signs, and much more that may impact a route via time or money. This knowledge gives users the ability to customize their routes and know more about their routes. Google Maps also combines its mapping capabilities with its search engine so users have access to more information and can find locations with ease. Users are also able to customize routes, like avoiding highways or tolls, for a more personalized experience. Google Maps also lets users pick different modes of transportation and adjust the route information accordingly. Thus, users can specify that they want route information based on a car, bike, walking, bus, and more.
Assessment of the Interaction
This interaction between Google Maps and the user is good and beneficial for users. Google Maps has a lot of information users can use and benefit from in a variety of ways. Users are able to search, find directions, customize routes, and more with ease.
ACTIVITY THEORY ANALYSIS
Subject
The primary users of Google Maps will be individuals who want to look up directions, view routes, find a particular location, view or search organizations (restaurants, grocery, etc.), and more.
Object
A visual, manipulative map interface will be the primary object being interacted with by individuals using Google Maps.
Instruments, tools, and Artifacts
The central application that is being viewed and interacted with is the visual, manipulative map interface of Google Maps. In addition to this, Google Maps has a text display for users to interact with various organizational information (like a store description, hours, reviews, images, etc). Users can also search for addresses, location names, organization names, and more.
Rules
The rules of Google Maps are primarily simply understood by the user. Google Maps offers a free-range interface in that users have access to a variety of options within the application at any time.
Community
Primary users in this community are individuals using Google Maps to learn locational information, find directions, or explore in various ways. Secondary users include businesses and organizations who may maintain their company's general information, address, service hours, and more within Google/Google Maps.
Division of Labor
The user is tasked with searching or inputting information to help the Google Maps application to give them the information they want. It is then the job of the application to take the information it has and display it to the user.
Outcome
The ultimate desired outcome of the system is a successful experience for the user. Success will vary depending on the individual's goals coming into the application. For example, success may look like an individual using Google Maps to get directions to the desired location, successfully using the directions and arriving at a destination, finding an organization's location or information, and more. In addition, success specific to directions will be showing the user an accurate route that fits an individual's needs best. For example, a user may want a route with no tolls, fewer stoplights, less traffic, or to avoid major potholes like this proposal suggests.
LITERATURE REVIEW
-
This publication used machine learning to take smartphone sensor data to detect potholes. It extracted smartphone sensor data from acceleration signals along three axes which resulted in high precision.
-
This publication uses smartphone accelerometer and gyroscope sensor data to detect potholes. A Neural Network model was trained to gather and analyze the data to distinguish potholes. The model they created has an accuracy of 94.78% in pothole detection.
-
This document outlines a 2017 patent by Google for pothole detection.
-
This publication analyzes the ability to use machine learning in pothole detection. They used Inception V3 and Transfer Learning. Inception V3 focuses on object identification and Transfer Learning analyzes data with the vehicle type and pothole shape. They also suggested the use of Neural Networks.
AREA OF GROWTH
Google Maps can improve its data usage and customization options offered to users. Google maps already has access to various sensors within phones like an accelerometer, gyroscope, and location data.
By using machine learning, Google Maps can take the sensor data from its users' phones to help identify potholes. Potholes are dangerous as they can cause damage to vehicles and cause vehicles to swerve, which can cause accidents.
With the use of machine learning and phone sensor data, Google Maps can identify potholes along roads. This information can be used to:
create map overlays so users can see potholes
allow users to report potholes
customize routes to avoid potholes
identify pothole location and severity for quicker reporting/repairs
MACHINE LEARNING TO IDENTIFY POTHOLES
Smartphone sensors to use:
Accelerometer
Gyroscope
Location
Machine learning methods to use:
Neural Networks
Transfer Learning
Inception V3
The accelerometer, gyroscope, and location data are able to detect and pinpoint the location of a pothole. These sensors help detect and identify specific movements and changes when cars pass over potholes.
This data can then be utilized by artificial intelligence to identify this data as representing a pothole. Using machine learning methods like neural networks, transfer learning, and inception V3 can be taught to read phone sensor data to determine what data likely shows potholes.
POTHOLE MAP OVERLAY
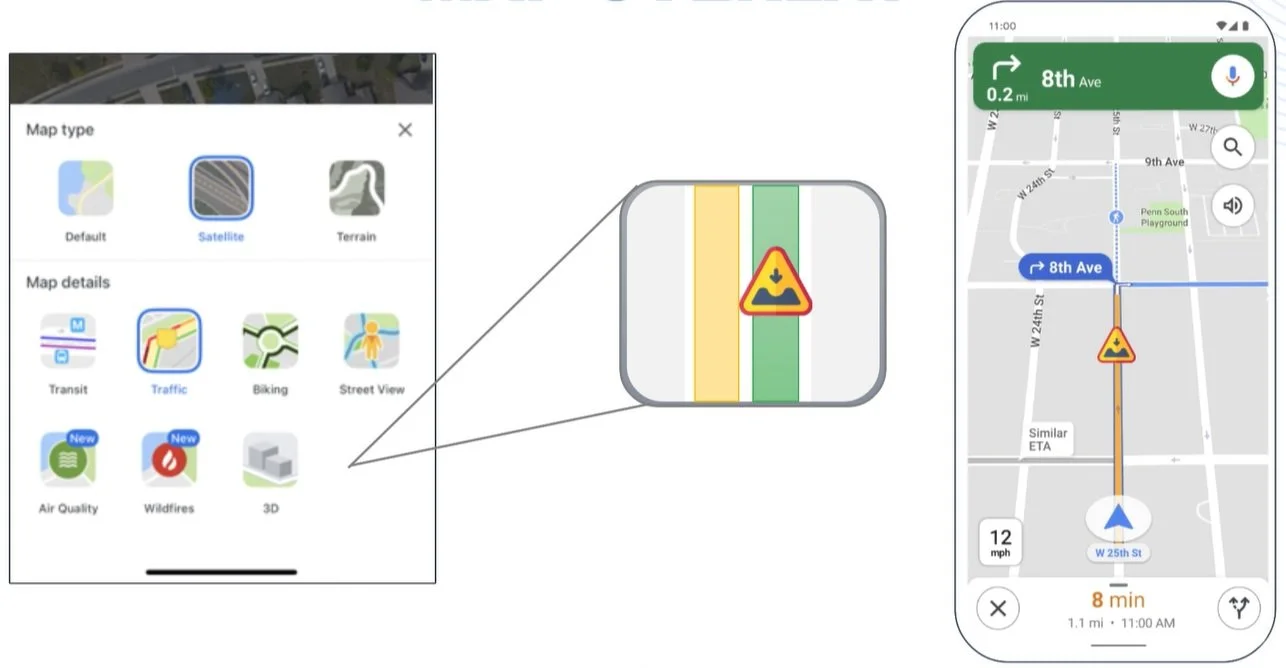
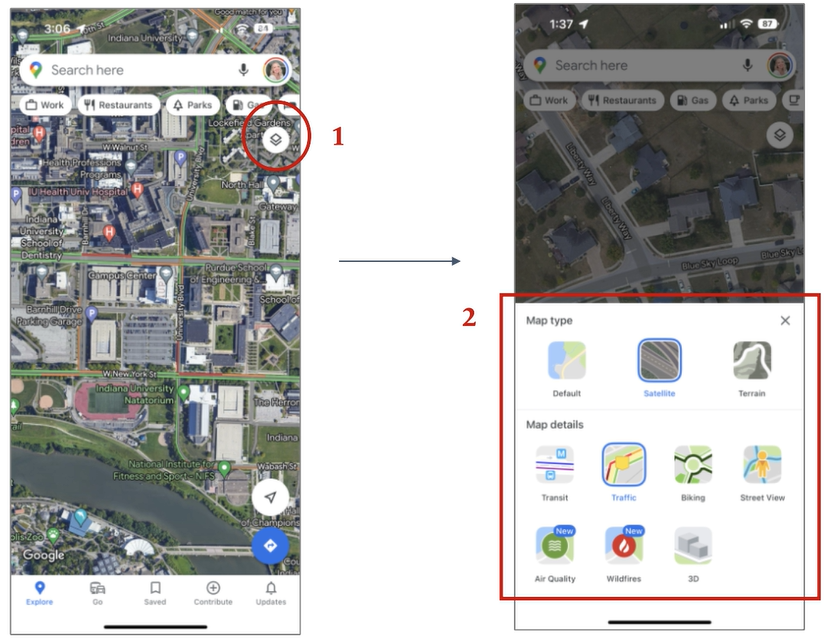
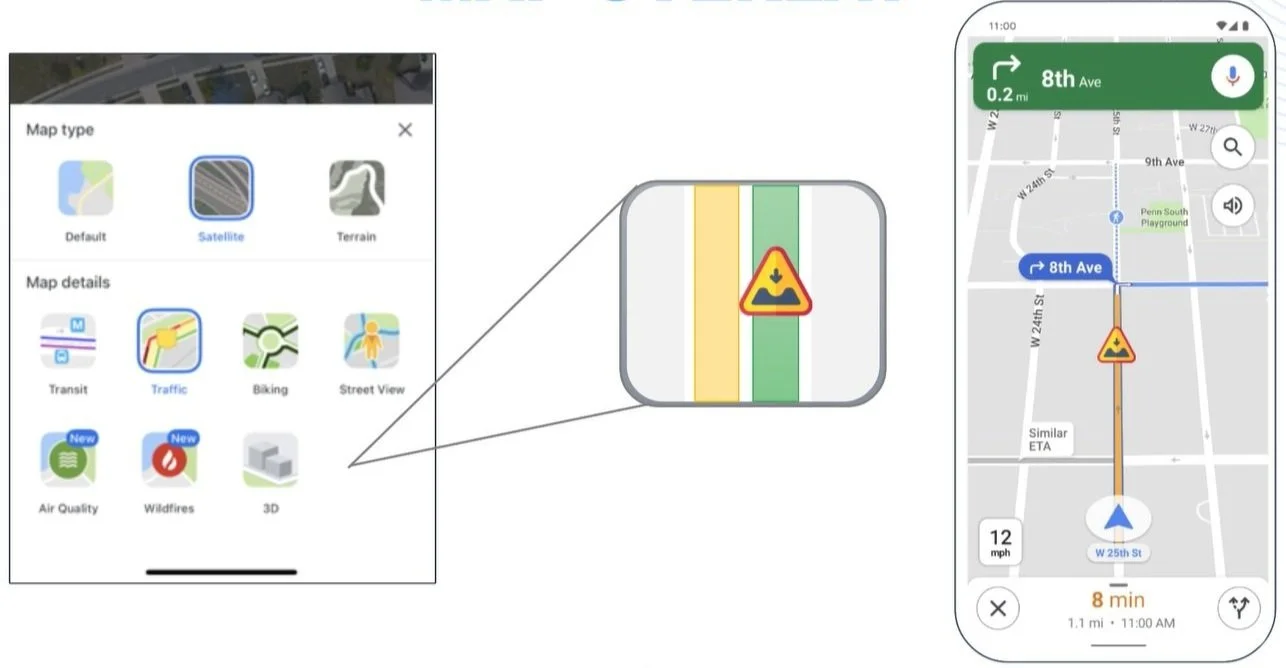
Currently, Google Maps offers a number of map overlays like transit, satellite, traffic, wildfires, and more as shown below.
With the new pothole detection system, Google Maps can add another map display potholes or add it to the current ‘traffic’ overlay. An example of adding it to the current traffic overlay is shown below.
If adding it to the ‘traffic’ overlay is chosen it should be a toggleable feature as in areas with a high number of potholes it will likely get in the way of being a default feature. Letting the user decide to toggle potholes on and off or view them as another overlay is a useful technique that lets the user customize their experience as desired within Google Maps. The optimal usage of this application will likely be to create another map overlay for potholes to avoid confusion and clutter. In order to display potholes, they can be indicated by semi-transparent circles that are color-coordinated by severity. Potholes can be colored similarly to the traffic overlay: green, orange, and red. Each color respectively increases the estimated severity of the pothole.
POTHOLE REPORTING
Users can report a number of things within Google Maps like speed traps, road closures, and more as shown below.
Potholes can be added as another item users can report within Google Maps. The report can let them quickly submit a pothole report based on their location or they can set a marker to a specific location and add information like its severity. This is beneficial not only in pothole identification but by taking multiple users' reports, the pothole detection system using smartphone sensors can also look at its data to see if it is being detected or to confirm a pothole.
ROUTING CUSTOMIZATION
While planning a route to a destination, users can customize the route they want to take by tolls, traffic, stoplights, and more. The new addition to this list will be potholes. Users can select a route with a minimal number or less severe potholes.
POTHOLE IDENTIFICATION FOR REPAIR
In order to speed up the process of pothole repair, Google Maps can give severity and locational information to the responsible party (government, state, other). This information can help give these entities a better understanding of road quality, problem areas, cost, and planning an optimal repair schedule. Ensuring potholes are found and fixed in an efficient manner can help minimize damage to vehicles and traffic accidents from pothole avoidance.
POTHOLE DETECTION APPLICATION ANALYSIS
Description
Google Maps can analyze smartphone accelerometers, gyroscopes, and other sensor data to detect movements that indicate a user has driven over a pothole. Machine learning methods and neural networks will be used to teach the system to analyze data and determine if the user likely drove over a pothole and the size and depth of the pothole. If it is determined likely a pothole, locational data will help pinpoint the pothole's location. This information can then be used by Google Maps to give a user more information about road conditions and routing options. In addition, users will also be able to report potholes so the system will also be able to view and check that information as well. Google Maps can then create a map overlay that displays potholes and their severity. Google Maps can also add pothole avoidance as another customization to their routing features so users can select routes with the least potholes. Lastly, Google Maps can take this data and give government or state officials access so that the identification and repair of potholes can be conducted at a more efficient pace.
Depth of Automation
The Pothole Detection System using Smartphone Sensors will ultimately be entirely automated. During creation and testing, the system will have to be monitored and taught to analyze the data it is receiving. Potholes can create different data depending on the vehicle interacting with them and the size and depth of the pothole. Ultimately the system will automatically take user data about their phone's sensors (like accelerometer, gyroscope, and others as needed). This data will be analyzed automatically for pothole detection. Once the system analyzes the data it will determine if there are any likely potholes on its own. High-likelihood potholes can be added to maps via locational data and identified for government or state officials to repair. The system can also take user reports of potholes and compare that to its findings.
SUMMARY OF EFFORT
Machine Learning:
Teach AI to identify potholes using phone sensor data
Use of machine learning methods such as: Neural Networks, Transfer Learning, Inception V3
Test various vehicles and potholes to ensure accuracy
Google Maps:
Create a pothole identification icon on the map
Create a pothole “map detail” overlay
Connect with AI so potholes can be identified and located
Reporting:
Add a pothole reporting option
Connect with AI to check against data gathered
USER FEEDBACK
I interviewed four users and discussed this new Google Maps feature with them. Overall the feedback was positive! Here is what they said:
Participant 1:
Likes the idea and thought the designs were well-made
The addition made sense with the rest of the features offered by Google Maps
Participant 2:
Travels to a variety of countries for work and felt that many places (like India) would benefit from this feature
Has a nice car and would use this feature to avoid roads with many potholes
Participant 3:
Liked the idea and felt that Google Maps should implement this
Felt they would use this feature in certain cities
Liked the designs
Participant 4:
Felt like it was a good idea and very easy to use
Since the sensor is available and being used already it makes sense to add this option
Likely would not user it, but thinks others would